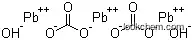1319-46-6 Usage
Description
Lead(II) carbonate basic, also known as basic lead carbonate or lead white, is an acid-soluble, heavy, white powder or crystalline substance that forms white hexagonal crystals. It is insoluble in water and alcohol but slightly soluble in carbonated water and soluble in nitric acid. When heated to 400 °C, it decomposes. Due to its high refractive index and weather fastness, it has a wide range of applications across various industries.
Uses
Used in Pigments and Coatings Industry:
Lead(II) carbonate basic is used as an excellent pearlescent pigment for creating pearlescent effects in pigments and coatings. It is also utilized in the production of inorganic pigments for paint and pigments.
Used in Printing and Ink Industry:
In the printing and ink industry, lead(II) carbonate basic is used for packaging paper, business cards, plastic cloth, and textiles, providing a high-quality finish and appearance.
Used in Paint Industry:
Despite the potential risks of lead poisoning and some limitations, such as vulnerability to thickening when used in white lead paint and a decline in whiteness when exposed to hydrogen sulfide, lead(II) carbonate basic is still used in the paint industry as white pigments for the production of original paint, anti-rust paint, and outdoor paint. It is also used as a raw material for ceramic glaze, painting, and cosmetics.
Used in Automotive and Furniture Industry:
Lead(II) carbonate basic is used in painting for cars, motorcycles, bicycles, and furniture, providing a stable coating film with excellent weather resistance and rust resistance.
Used in Plastic Industry:
In the plastic industry, basic lead carbonate can be used as a vinyl chloride plastic stabilizer for the production of pearlescent plastic and pearlescent paint.
Used in Ceramic Glaze and Exterior Paint:
Lead(II) carbonate is also used in the formulation of ceramic glaze and exterior paint, enhancing their durability and appearance.
Used in Oil Paints, Water Colors, and Cement:
Lead(II) carbonate basic can be used as a pigment in oil paints and watercolors, as well as in the production of cement.
Used in Putty and Paper Production:
It is also utilized in the making of putty and lead carbonate paper, providing a unique texture and appearance.
Used in Parchment Processing:
Lead(II) carbonate basic is employed in the processing of parchment, contributing to its distinctive qualities.
Solubility in water(g/100ml)
Dissolved grams per 100 milliliters of water:
7.269 × 10-5/20 °C Toxicity
Preparation
1. Chemical method: adding carbon dioxide, deionized water into reaction solution prepared by lead acetate, lead oxide and deionized water. After reaction, then by precipitation, added with nitrocellulose pulp slurry, precipitation, crystallization, centrifugal dehydration, washed with alcohol, drying, the basic lead carbonate is obtained. Alcohol waste liquid is treated and recovered. The reaction equation is: Pb(Ac)2+PbO+H2O→Pb(Ac)2?Pb(OH)2;
3[Pb(Ac)2?Pb(OH)2]+2CO2→3Pb(Ac)2+2PbCO3?Pb(OH)2+2H2O
2. Acetic acid method: mix yellow lead, acetic acid and water together in the mother liquor tank, and the concentration of the mixture of lead oxide is 230~250 g/L. Suspend the mixture with stirring; keep warm for 3h in the 90 ℃? leading to the formation of basic lead acetate; clarify and carbonize with purified carbon dioxide; when 85% lead hydroxide in the basic lead acetate is carbonized, that is the end of the reaction; and then by precipitation, centrifugal separation, with oil and alcohol washing and drying, basic lead carbonate products is made. In addition, the separated mother liquor can be recycled. The reaction equation is: 2PbO + 2HAc → Pb (Ac) 2 ? Pb (OH) 2
3[Pb(Ac)2?Pb(OH)2]+2CO2→3Pb(Ac)2+2PbCO3?Pb(OH)2+2H2O.
Preparation
Many commercial processes have been developed for manufacturing basic lead carbonate. These include: Thomson-Stewart process, Carter process, and Dutch process. The method of preparation involves treating lead with acetic acid vapors in the presence of carbon dioxide at 60°C. In the Thomson-Stewart process, finely divided lead monoxide or lead metal is mixed with water to give aqueous slurry, which is then mixed with acetic acid in the presence of air and carbon dioxide. All these processes are slow, taking weeks to obtain products of desired composition. Basic lead carbonate also is precipitated by dissolving lead monoxide in lead(II) acetate solution, and treating the solution with carbon dioxide. It also is produced by electrolysis of sodium nitrate or sodium acetate using lead anode and then precipitating out the product by adding sodium carbonate..
Toxicity
Early symptoms of poisoning is that lead linear appearing in the edge of the gums and urinary poisoning. For chronic poisoning, it has changes in the nervous system, the emergence of debilitating syndrome, encephalopathy, dysmotility, changes in the blood system, metabolic and endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal changes and changes in the cardiovascular system.
A maximum allowable concentration of lead and lead inorganic compounds is 0.01 mg/m3 and 0.0007 mg/m3 in an average working day.
When the poisoned suffered colic, he should receive subcutaneous injection of atropine, morphine, and intravenous injection of magnesium sulfate, sodium thiosulfate, calcium chloride. Masks blocking 95% to 97% of lead dust is allowable when working; when in the environment of high vapor concentration, you can use the filter gas mask for a forced supply of fresh air. When the poisoned ones suffered colic, he should receive subcutaneous injection of atropine, morphine, and intravenous injection of magnesium sulfate, sodium thiosulfate, calcium chloride.
Production Methods
Basic Lead Carbonate is produced by several methods, in which soluble lead acetate is treated with carbon dioxide. For example, in the Thompson-Stewart process, an aqueous slurry of finely divided lead metal or monoxide, or a mixture of both, is treated with acetic acid in the presence of air and carbon dioxide. High quality, very fine particle-size basic lead carbonate is produced, ranging in carbonate content from 62 to 65% (vs 68.9% PbCO3, theoretical).
Flammability and Explosibility
Nonflammable
Check Digit Verification of cas no
The CAS Registry Mumber 1319-46-6 includes 7 digits separated into 3 groups by hyphens. The first part of the number,starting from the left, has 4 digits, 1,3,1 and 9 respectively; the second part has 2 digits, 4 and 6 respectively.
Calculate Digit Verification of CAS Registry Number 1319-46:
(6*1)+(5*3)+(4*1)+(3*9)+(2*4)+(1*6)=66
66 % 10 = 6
So 1319-46-6 is a valid CAS Registry Number.
InChI:InChI=1/CH2O3.Pb.4H/c2-1(3)4;;;;;/h(H2,2,3,4);;;;;/q;+2;;;;/p-2/rCH2O3.H4Pb/c2-1(3)4;/h(H2,2,3,4);1H4/q;+2/p-2