- Min.Order :0 Metric Ton
- Purity: 98-102%
Keywords
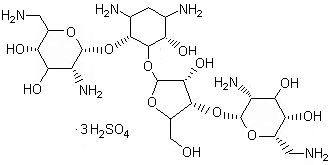
Neomysin Sulfate
Quick Details
- Appearance:
- Application:
- PackAge:
- ProductionCapacity:|Metric Ton|Day
- Storage:
- Transportation:
Superiority:
Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic found in many topical medications such as creams, ointments, and eyedrops. The discovery of neomycin dates back to 1949. It was discovered in the lab of Selman Waksman, who was later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and medicine in 1951. Neomycin belongs to aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more aminosugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Due to the inherent oto- and nephrotoxicity of these substances, systemic use has declined, as safer alternatives have become available.
Details:
Neomycin is typically used as a topical preparation, such as Neosporin. It can also be given orally, where it is usually combined with other antibiotics. Neomycin is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and has been used as a preventive measure for hepatic encephalopathy and hypercholesterolemia. By killing bacteria in the intestinal tract, it keeps ammonia levels low and prevents hepatic encephalopathy, especially prior to GI surgery. It has also been used to treatsmall intestinal bacterial overgrowth. It is not given intravenously, as neomycin is extremely nephrotoxic (causes kidney damage), especially compared to otheraminoglycosides. The exception is when neomycin is included, in very small quantities, as a preservative in some vaccines - typically 0.025 mg per dose.[1]
You Might Also Like
-
Methyl Carprofenate China supplier
CAS NO:53716-49-7
-
Metformin Hydrochloride China factory
CAS NO:1115-70-4
-
Olsalazine Sodium China supplier
CAS NO:50847-11-5
-
Robenidine HCL China factory
CAS NO:25875-50-7
-
Oxolinic Acid China manufacturer
CAS NO:14698-29-4
-
Furaltadone Hcl China factory
CAS NO:139-91-3
Related Searches
About|Contact|Cas|Product Name|Molecular|Country|Encyclopedia
Message|New Cas|MSDS|Service|Advertisement|CAS DataBase|Article Data|Manufacturers | Chemical Catalog
©2008 LookChem.com,License: ICP
NO.:Zhejiang16009103
complaints:service@lookchem.com Desktop View