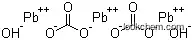-
Name
Lead(II) carbonate basic
- EINECS 215-290-6
- CAS No. 1319-46-6
- Density 6,14 g/cm3
- Solubility insoluble in water
- Melting Point 400 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- Formula 2PbCO3.Pb(OH)2
- Boiling Point 333.6 °C at 760 mmHg
- Molecular Weight 775.63
- Flash Point 169.8 °C
- Transport Information UN 2291 6.1/PG 3
- Appearance dense white powder
- Safety 53-45-60-61
- Risk Codes 61-20/22-33-50/53-62
-
Molecular Structure
-
Hazard Symbols
 T;
T;  N
N
- Synonyms Silver White;Almex;Bis(carbonato)dihydroxytrilead;Lead,bis[carbonato(2-)]dihydroxytri-;Lead subcarbonate;White lead;C.I. Pigment White 1;Basic carbonate white lead;Berlin White;Lead Carbonate,Basic;Lead(II) carbonate, basic;
- PSA 166.84000
- LogP -6.39000
Lead(II) carbonate basic Specification
The Lead hydroxide carbonate, with the CAS registry number 1319-46-6 and EINECS registry number 215-290-6, has the IUPAC name of lead(2+) dicarbonate dihydroxid. And the molecular formula of this chemical is 2PbCO3.Pb(OH)2. It is a kind of dense white powder, and belongs to the following product categories: Inorganics; Lead Salts; Metal and Ceramic Science; Salts; Analytical Reagents; Analytical Reagents for General Use; Puriss.
The physical properties of Lead hydroxide carbonate are as following: (1)#H bond acceptors: 8; (2)#H bond donors: 6; (3)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 0; (4)Polar Surface Area: 126.38 Å2.
Preparation of Lead hydroxide carbonate: Pass the carbon dioxide in to the reaction solution which contains leadacetate, massicot and deionized water. Then after a series of sedimentation, crystallization, dehydration, washing and drying, you can get the product. And the reactions equation are:
Pb(Ac)2 + PbO + H2O → Pb(Ac)2.Pb(OH)2
3[Pb(Ac)2.Pb(OH)2] + CO2 → 3Pb(Ac)2 + 2PbCO3.Pb(OH)2 + 2H2O
Uses of Lead hydroxide carbonate: It is a white paint used in the production of anticorrosion paint and outdoor paint. And it is also used as the raw material of cosmetics, colored glaze and dope. Besides, it is the stabilizing agent for vinyl chloride plastic, and also used in the tin-lead plating.
You should be cautious while dealing with this chemical. It is harmful by inhalation and if swallowed, and has the danger of cumulative effects. It may also cause harm to the unborn child. In addition, it is very toxic to aquatic organisms, and may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. Therefore, you had better take the following instructions: Avoid exposure - obtain special instruction before use; In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible); This material and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste; Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions safety data sheet.
You can still convert the following datas into molecular structure:
(1)SMILES: C(=O)([O-])[O-].C(=O)([O-])[O-].[OH-].[OH-].[Pb+2].[Pb+2].[Pb+2]
(2)InChI: InChI=1/2CH2O3.2H2O.3Pb.6H/c2*2-1(3)4;;;;;;;;;;;/h2*(H2,2,3,4);2*1H2;;;;;;;;;/q;;;;3*+2;;;;;;/p-6/r2CH2O3.2H2O.3H2Pb/c2*2-1(3)4;;;;;/h2*(H2,2,3,4);5*1H2/q;;;;3*+2/p-6
(3)InChIKey: RZCMDZAYEFUPDZ-CULGMVJYAU
Related Products
- Lead(II) acetate
- Lead(II) arsenite
- Lead(II) azide
- Lead(II) bromide
- Lead(II) carbonate basic
- LEAD(II) CHLORITE
- Lead(II) cyanide
- Lead(II) diethyldithiocarbamate
- Lead(II) EDTA complex
- Lead(II) fluorosilicate
- 13194-67-7
- 13194-68-8
- 13194-69-9
- 13194-70-2
- 13194-71-3
- 131947-13-2
- 13194-73-5
- 13195-50-1
- 13195-64-7
- 13195-66-9
Hot Products
About|Contact|Cas|Product Name|Molecular|Country|Encyclopedia
Message|New Cas|MSDS|Service|Advertisement|CAS DataBase|Article Data|Manufacturers | Chemical Catalog
©2008 LookChem.com,License: ICP
NO.:Zhejiang16009103
complaints:service@lookchem.com Desktop View