-
Name
Neotame
- EINECS 253-404-6
- CAS No. 165450-17-9
- Article Data5
- CAS DataBase
- Density 1.133 g/cm3
- Solubility Sparingly soluble in water, very soluble in ethanol
- Melting Point 80.9-83.4 °C
- Formula C20H30N2O5
- Boiling Point 565.3 °C at 760 mmHg
- Molecular Weight 378.469
- Flash Point 295.7 °C
- Transport Information
- Appearance White or off white crystalline powder
- Safety 24/25
- Risk Codes
-
Molecular Structure
- Hazard Symbols
- Synonyms L-Phenylalanine,N-[N-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-L-a-aspartyl]-,1-methyl ester;
- PSA 104.73000
- LogP 2.53780
Synthetic route

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With hydrogen; palladium 10% on activated carbon In methanol; water at 20℃; for 6h; | 85% |
| With hydrogen; palladium on activated charcoal under 1551.44 Torr; for 12h; Condensation; reduction; room t.; | 56% |
| With hydrogen; palladium on activated charcoal In methanol at 20℃; under 1551.44 Torr; for 12h; Hydrogenation; reductive alkylation; | 56% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With 5%-palladium/activated carbon; sodium hydrogencarbonate In methanol at 30 - 40℃; under 4500.45 Torr; for 6h; Time; Pressure; |
-
-
165450-17-9
neotame

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| With sodium hydroxide In methanol; water at 20℃; for 1.5h; | 79% |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In water at 70℃; for 1h; Heating / reflux; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In methanol at 20℃; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In methanol at 20℃; |

| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
| In methanol at 20℃; |
Neotame Chemical Properties
IUPAC Name: (3S)-3-(3,3-Dimethylbutylamino)-4-[[(2S)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid
Molecular Formula: C20H30N2O5
Molecular Weight: 378.46 g/mol
Refraction indexis of Neotame (165450-17-9): 1.521
Surface Tension: 43.6 dyne/cm
Density: 1.133 g/cm3
Flash Point: 295.7 °C
Enthalpy of Vaporization: 89.33 kJ/mol
Boiling Point: 565.3 °C at 760 mmHg
Vapour Pressure: 1.29E-13 mmHg at 25 °C
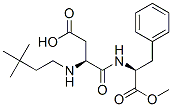
The molecular structure of Neotame (165450-17-9):
Neotame Uses
Neotame (165450-17-9) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for general use in July 2002, but is not yet widely used in food products. Neotame also is approved for use in Australia and New Zealand. Neotame is assigned the International Numbering System (INS) food additive code 961.
Neotame Specification
The chemical synonyms of Neotame (165450-17-9) are Neotame (200 MG) ; Neotame ; N-(N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L-alpha-aspartyl)-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester ; L-phenylalanine, N-[N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L-.ALPHA.-ASPARTYL]-, 1-methyl ester ; and N-[N-(3,3-Dimethylbutyl)-L--aspartyl]-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester .
Neotame (165450-17-9) is an artificial sweetener made by NutraSweet that is between 7,000 and 13,000 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar). In the European Union it is known by the E number E961. Neotame (165450-17-9) is moderately heat stable and extremely potent. Neotame is rapidly metabolized, completely eliminated, and does not accumulate in the body.
The major metabolic pathway is hydrolysis of the methyl ester by esterases that are present throughout the body, which yields de-esterified neotame and methanol. Because only trace amounts of neotame are needed to sweeten foods, the amount of methanol derived from neotame is much lower than that found in common foods, such as fruit and vegetable juices.
The product is attractive to food manufacturers as its use greatly lowers the cost of production compared to using sugar or high fructose corn syrup (due to the lower quantities needed to achieve the same sweetening) while also benefitting the consumer by providing fewer "empty" sugar calories and a lower impact on blood sugar.
It is chemically similar to the artificial sweetener aspartame, but it is used at vastly lower levels and is more stable. Chemically, it has a 3,3-dimethylbutyl group attached to the amino group of the aspartic acid portion of the molecule. Peptidases, which would typically break the peptide bond between the aspartic acid and phenylalanine moieties, are effectively blocked by the presence of the 3,3-dimethylbutyl moiety, thus reducing the production of phenylalanine, thereby making its consumption by those who suffer from phenylketonuria safe.
About|Contact|Cas|Product Name|Molecular|Country|Encyclopedia
Message|New Cas|MSDS|Service|Advertisement|CAS DataBase|Article Data|Manufacturers | Chemical Catalog
©2008 LookChem.com,License: ICP
NO.:Zhejiang16009103
complaints:service@lookchem.com Desktop View

